Introduction
Figure 1: Arenales del Sol WWTP
The Arenales del Sol WWTP, located in Alicante in the Mediterranean region of Spain, combines biological treatment with nutrient removal with a submerged MBR system fitted with flat sheet (FS) ultrafiltration membranes, with an average treatment capacity of 10,000 m3/d (10 MLD). The plant provides high quality treatment to highly variable seasonal sewage inflow due to the nature of this popular coastal region, where second homes and golf courses attract visitors during the summer months and winter and Easter vacation periods.
This seasonal feature became a major challenge during the commissioning of this relatively large MBR plant in a short space of time and with very little contingency, demanding specific operational strategies.
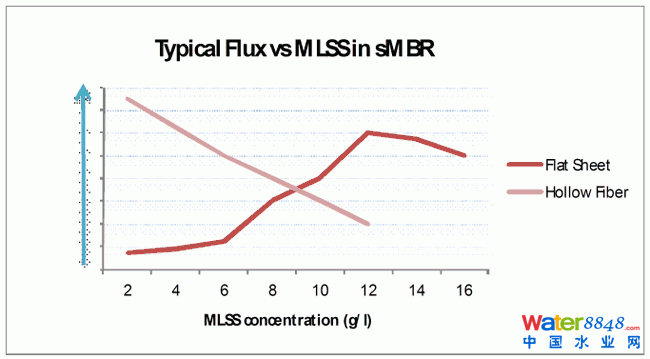
Figure 2: Specification – Arenales del Sol WWTP
Typical commissioning challenges of an MBR
Many WWTPs fitted with MBR technology have experienced severe difficulties during the commissioning and start-up phases of the project, specifically because operational problems are normally manifested as failure to meet the hydraulic load, rather than achieve the required level of purification. This demands that membrane fouling and clogging is minimised as much as possible, through removal of fine solids and reduction of EPS or dissolved organic carbon levels in the sludge. Also, the variation of operational parameters such MLSS concentration, peak fluxes and aeration volume are known to exacerbate fouling and clogging, as well as the sludge floc structure.
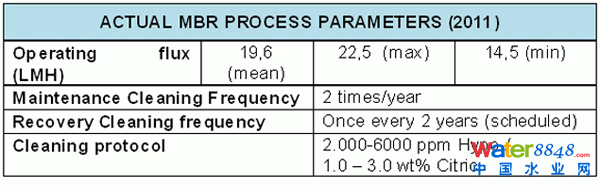
Figure 3: Actual MBR process parameters
Various challenges arise during MBR commissioning, including:
-
rapid membrane fouling due to insufficient biomass concentration, unhealthy micro-organism populations, excessive EPS formation or membrane blocking
-
overflowing tanks from heavy foaming events (with subsequent biomass loss) or membrane clogging
-
under-spec treated water quality prior to the biological conditions reaching the design values, and specifically the MLSS concentration
-
impaired treatment from incomplete tasks from commissioning, such as clean water testing, PID control adjustment, etc
-
membrane clogging or ragging due to unscreened seeding sludge
-
membrane damage due to abrasion from construction materials, such as metal shards from thread tapping not removed from the MBR tanks
-
sludge settling due to blower failure
-
membrane over- or under-aeration due to incomplete PID blower testing or incorrect blower design.
All the activities planned for the commissioning of this WWTP aimed to minimise or avoid the above, by applying knowledge available from a number of published case studies.
Figure 4: The MBR tanks at Arenales del Sol WWTP
Commissioning requirements, hollow fibre versus flat sheet systems
Sludge seeding in biological and MBR tanks can become challenging in medium to large municipal WWTPs. Typically, the anoxic and oxic reactor volumes are usually too large and unchambered to be filled with rather concentrated sludge from other WWTPs in a single step. Equally difficult and expensive is to truck in excess recirculation sludge from other secondary decanters to achieve a high MLSS concentration in the MBR tanks.
On-site biomass augmentation is thus unavoidable for any medium to large MBR plant, and the target MLSS concentration will depend on the membrane configuration: 5-8 g/l (or 10-12 g/l for short periods) for an HF configuration compared with 12 to 15 g/l for the FS. It follows that target biomass conditions are more rapidly attained for HF systems. Moreover, as often observed in MBR literature, FS membranes experience major fouling at lower MLSS from small pin-floc structures causing rapid pore blocking more rapidly. At higher MLSS levels and correspondingly larger flocs, the sludge-scouring air mixture provides greater higher shear and so an improved cleaning efficiency at higher MLSS concentrations (up to 18 g/l) than at lower.
In the case of HF systems, the initial MLSS concentration is not considered as important during commissioning, since they demonstrate good best filtration performances at sludge seeding concentrations (2 to 6 g/l).

Figure 5: Typical flux versus MLSS in sMBR

Figure 6: Clean water testing
It was important to reduce the risk of initial fouling at the low MLSS concentrations to avoid downtime for chemical cleaning. However, since the existing WWTP was not meeting effluent discharge standards, the new plant had to be ready for work with full flow treatment warranties in a shortened time. Given the time constraints the project was under, a minimum MLSS concentration of only 6-7 g/l was deemed necessary prior to operation with the FS MBR membranes.
All ancillary equipment to the MBR (blowers, pumps, PLC, etc) was fully tested with clean water.
Fouling control strategies during start-up: Biomass development
Biological degradation of the sludge in the reactors is required not only to meet effluent discharge standards but also to avoid membrane fouling by excessive unoxidised BOD levels. Time restrictions associated with the commissioning required both a stable biomass and a ready-for-business MBR system at the design conditions of 12.5-15 g/l within 8-10 weeks.
Unfortunately, since only about 30% of design inflow was being received at the time, there was a shortage of carbon for natural bio-augmentation. Biomass augmentation was thus achieved using the anoxic and oxic tanks in one (of two) of the treatment lines in an sequencing batch mode, with supernatant being regularly withdrawn so as to increase the MLSS without decharging the solids (thus increasing the SRT).
The plant was fed both with untreated sewage pumped from the existing plant at a reduced loading rate and sugar cane residues as an additional carbon source. Additionally, small volumes of hydrophyliced bacteria were added in the first few days to rapidly increase the available micro-organism population in the tanks. This strategy allowed for a controlled seeding process while closely examining biomass species under the microscope.
All sludge fed into the new plant was mesh filtered in the new rotary drum screens (punch-hole, 1mm) for failsafe operation of the membranes.
Modelling software (WEST) was used to simulate biomass growth in the biological tanks. As it turned out, WEST predictions were quite accurate in assessing the actual biomass growth rate during start-up. The time employed in seeding and concentrating the sludge was used to calibrate the input data for the modelling software.
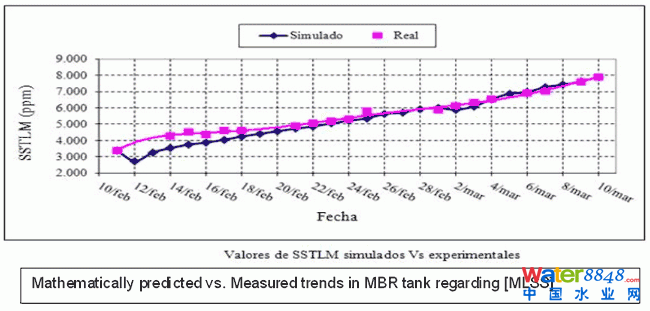
Figure 7: Mathematically predicted versus measured trends in MBR tank regarding [MLSS]
Fouling control strategies during start-up: Flux control
Flux control is crucial for fouling control. It is well known that if flux is maintained below a certain critical value (known as critical flux), it is possible to ensure stable operation with little or negligible increase in TMP for longer periods, and hence reduce cleaning frequency. It is also true, however, that this critical flux is unique to every MBR plant and process water characteristics, and it is usually only ascertained through trial and error experimentation under design operational conditions (in this case, 12.5 g/l at 22-28 LMH). Strict flux control during commissioning stage is thus essential to avoid accelerated fouling, particularly when using FS system configurations.
Flux values employed prior to reaching the design conditions were kept conservative, particularly at around 6-7 g/l MLSS when operation was kept well below the critical flux. Average biomass temperature at start-up was slightly above 16ºC.
Since commissioning time was getting closer and filtration had to be resumed promptly prior to the Easter vacation period, filtration was started with a low MLSS of 6.5 g/l and a flux below 8 LMH, with a maximum allowed emergency flux of 10 LMH. The operational flux allowed at each of the commissioning phases (see below) was chosen according to previous experiences with the chosen membrane technology.
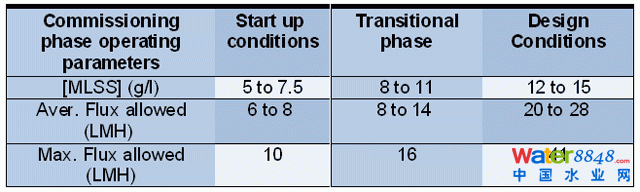
Figure 8: Operational flux at each of the commissioning phases
This filtration time prior to commissioning, even at these low fluxes (design flux was 22 LMH) allowed for both biomass concentration and biomass acclimatation while reaching the more acceptable MLSS levels above 10 g/l. Again, the WEST modelling software was employed to forecast biomass growth and hence inform the initiation of full-flow start-up of the plant.
Fouling control strategies during start-up: Air scouring control and optimisation
The beneficial effects of air scouring to control fouling at the membrane surface of flat sheet membranes is well documented. Typically, it is assumed that there is a linear relationship between membrane flux (Lwater/m2/h) and the air scouring rate (Nm3/h/m2), within some limits above which this positive influence of higher air volume per unit membrane area is no longer observed. The designed air scouring range for the membranes was from 0.42-0.6 Nm3/h/m2 – typical for a double-deck Toray system.
Initially, the MBR control system had been programmed so as to reduce the energy consumption related to air scouring according to a flux/TMP related algorithm; that is, employing the lowest air scouring rate possible so as to maintain a flux below the critical flux value. This type of control assumed a steady sludge concentration within the design limits (12-15 g/l), as opposed to the low solids concentration operation required at the start-up phase. For this reason, it was decided to re-program the SCADA control software so that it would allow for an additional operational mode with low MLSS, where the highest air scouring rate could be employed when [MLSS] in the MBR tanks was below a critical value of 8 g/l.

Figure 9: MBR pumps at Arenales del Sol
Also, during low or no inflow periods to the plant, the MBR would allow for intermittent aeration every 30 minutes to maintain aerobic conditions, avoiding sludge settling at the bottom of the tanks and between the membrane plates. When not in operation, all membrane lanes were aerated for 2.5 minutes every 25 minutes. During low inflow periods, the eight MBR lanes were operated alternatively in pairs.
Finally, a submersible mixer was installed in each MBR lane not fitted with MBR modules (until second commissioning phase) to keep biomass in suspension, while a minimum 200% recirculation was maintained.
Fouling control strategies during start-up: Polymer dosing
To minimise potential fouling at initial low MLSS, it was also decided to dose a synthetic cationic polymer, (MPE 50, Nalco) designed to suppress membrane fouling. This product has shown good results in increasing critical flux at other existing MBRs worldwide at low temperatures, as per the MBR consultants’ experience, and also suppresses foaming. It was not possible at the time of commissioning to evaluate fully the beneficial effects of the addition of this polymer, since there was a simultaneous temperature increase in the sludge at the time of dosing (see graph).
The dosage of MPE 50 was initiated at 4 g/l MLSS and was stopped shortly before reaching 9 g/l. The use of this product was considered, however, a viable option to reduce fouling – or enhance flux – and it was subsequently included in the plant’s O&M guidelines as an emergency strategy to improve plant’s overall performance during storm events, load changes or significant temperature decrease.
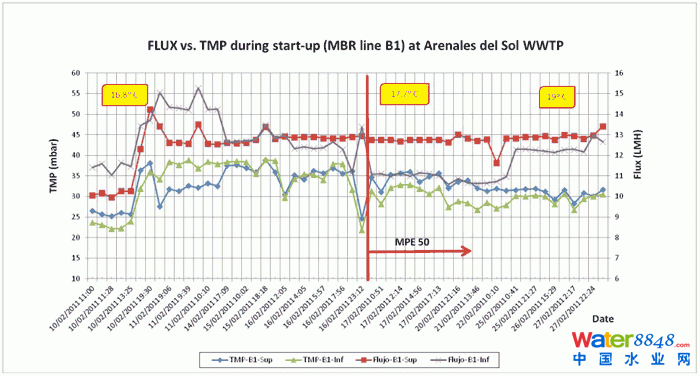
Figure 10: Flux versus TMP during startup (MBR line B1) at Arenales del Sol WWTP
Fouling control strategies during start-up: Foaming
Foaming is a common issue in biotreatment processes and there are a large number of management strategies, yet these are not always put into practice. Historically, there have been many MBR plants installed without foaming removal or control systems in their designs which subsequently experienced problems during foaming events, with foam sometimes overflowing into the biological tanks.
The occurrence of foam at start-up and operational stages differs both in its origin and also in its magnitude. The release of the hydrophilic agent the membranes are coated with for preservation during storage may cause a very light and clear foam, which disappears within hours once filtration conditions start. Another type of foaming that can happen at the same time is of biological origin and can arise from low temperatures, insufficient organic loads, a non-acclimatised biomass or excessive chemical cleanings.
Foaming may be exacerbated when the biological process in the aerobic/anoxic tanks and the MBR is interrupted due to the typical PID and equipment adjustments that take place during start-up. As a result, extensive inactivation of micro-organisms will lead to foaming due to proteinaceous DNA release from dead cells. Finally, foaming occurrence during normal and stable operation of MBRs is also common due to the long SRTs, yet this foam type tends to be naturally controlled at large municipal plants as long as foam is not “trapped” in the reactor.
At Arenales del Sol, foaming issues were taken into consideration when designing the biological tanks, ensuring that there was always an overflow from anoxic tanks through to the MBR chambers and into the recirculation chamber. Any foaming event eventually ends up at the MBR lanes, where an overflow weir directs all recirculating sludge (and foam) into a channel fitted with a simple foam removal system that operates with two manually operated gates. All foam removed is accumulated in a sump fitted with submersible pumps, from where it can then be sent to the sludge dewatering system, or back into the recirculation pipeline into the anoxic tanks.
Conclusions
The Arenales del Sol plant was, at the time of commissioning, under some of the typical pressures found in municipal WWTPs in coastal regions. There was an urgency to have the plant fully working at certain dates and there was no room for error in either the water quality to be provided or in reliance on the existing plant which could no longer provide efficient treatment.
The previous MBR knowledge of the contractor, MBR system integrators and technical assistance ensured a rapid commissioning with minimal deviations from the planned schedule over a period of eight weeks. The whole WWTP was designed with a great amount of contingency equipment and fully orientated towards MBRs.
The WEST modelling software was helpful in forecasting potential biological process pitfalls prior to the plant attaining design conditions and aided greatly in the planning of sludge seeding and biomass acclimatation. It also provided useful strategies for operation, as the software was also used to simulate different inflow scenarios throughout the year.
Finally, a great deal of care and planning was put into the commissioning and start-up phases of the project, with various preventive fouling control techniques enforced with the sole aim of reducing plant downtime for maintenance cleaning and ensuring full flow treatment capability for the critical first few months.